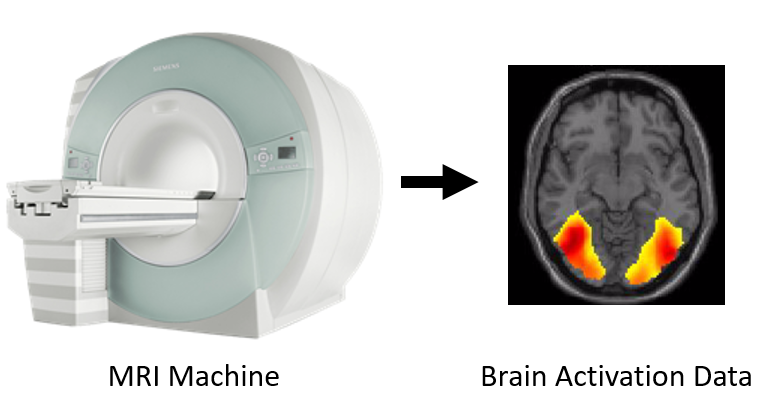
fMRI
Functional magnetic resonance imaging or functional MRI (fMRI) measures brain activity by
detecting changes associated with blood flow. This technique relies on the fact that cerebral
blood flow control to brain is local—when an area of brain gets
activated, the blood flow increases just in that area. Functional MRI picks up this increase
in blood flow producing higher fMRI response when neural activity increases.
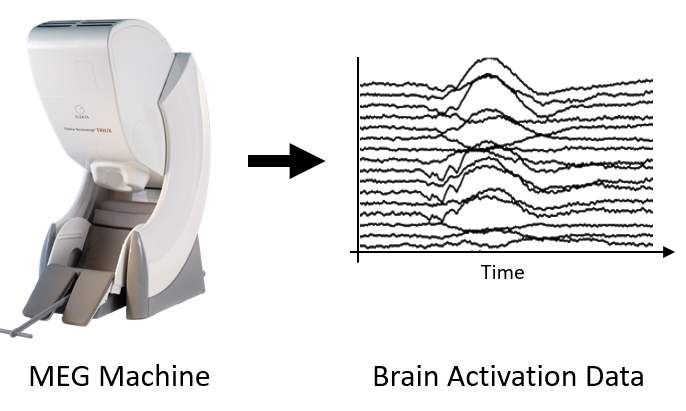
MEG
Magnetoencephalography (MEG) is a neuroimaging technique that uses an array of sensors
positioned over the scalp that are extremely sensitive to tiny changes in the magnetic
fields produced by small changes in the electrical activity within the brain. It is,
therefore, a direct measurement of neural activity.